Types of ABA
What does ABA look like at KBS?
We are not your typical ABA company. We specialize in Focused ABA verse Comprehensive ABA. The behavior of interest addressed during focused ABA treatment is narrower in scope than target behaviors addressed during comprehensive ABA treatment. Examples of behavioral targets that may be appropriately addressed in focused ABA treatment are: cooperation within specific home, educational or medical settings, specific self-help or adaptive targets, participation in specific leisure or family activities, etc. Socially significant behavior change occurs by teaching a more efficient and appropriate behavior which replaces the inappropriate or problem behavior.
Focused ABA treatment consists of:
· A treatment plan is developed based upon assessment which determines the function the target behavior serves in the learner’s environment
· Intensity and duration of treatment is based upon individual learner needs and severity of the behavior
· Treatment occurs during multiple 1 hour to 3 hour sessions per week dependent on individualized client needs
· Treatment decisions are based upon on-going data collection and error analysis
· Re-assessment occurs as determined by individual progress on treatment goals
· The majority of treatment hours are implemented by highly trained behavioral technician or Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA)
· Parent training in principles and procedures of ABA occurs on an on-going basis in our Parent Workshop as it relates the client’s increase in targeted skill areas and reduction of problem behavior.
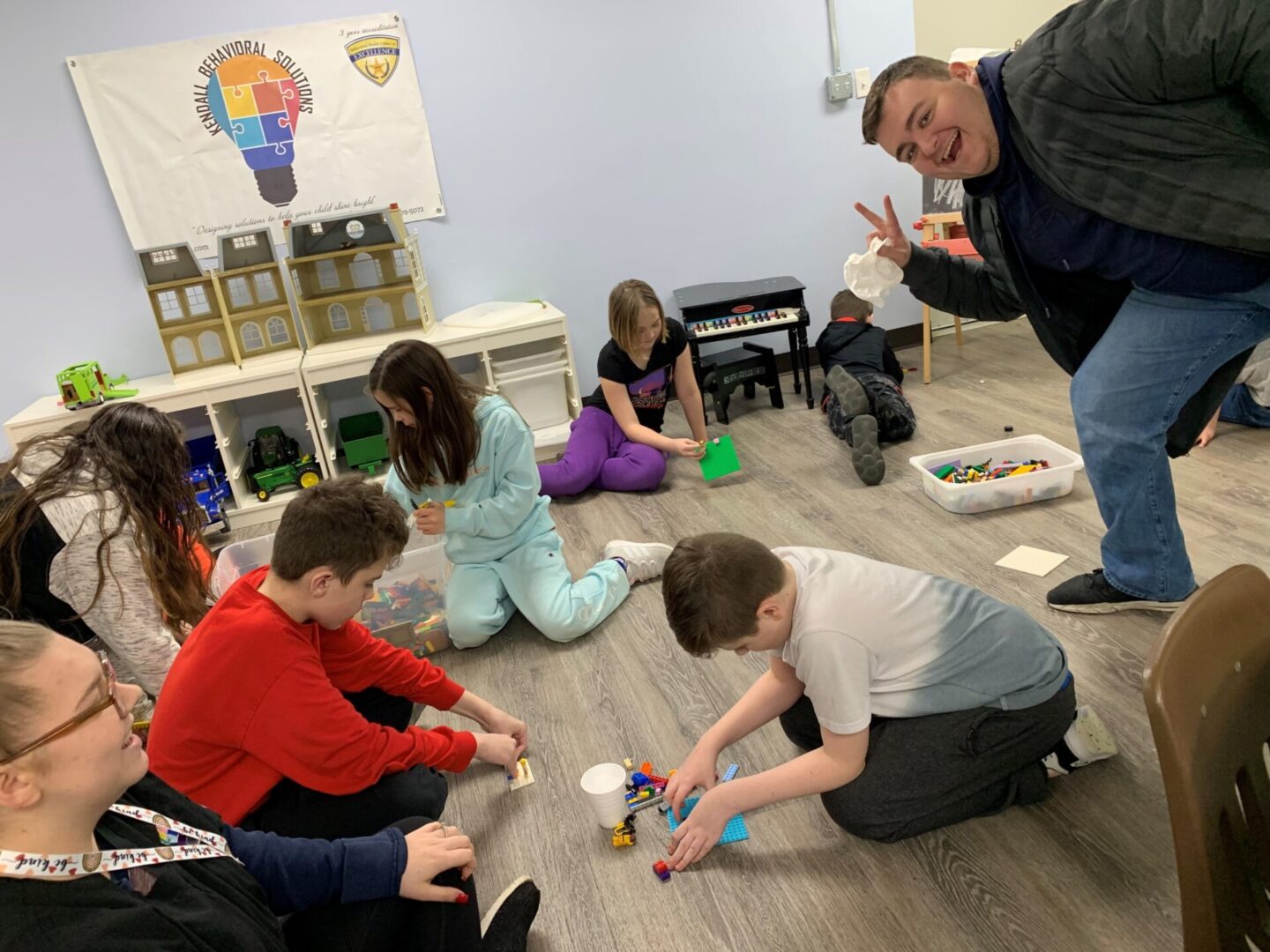

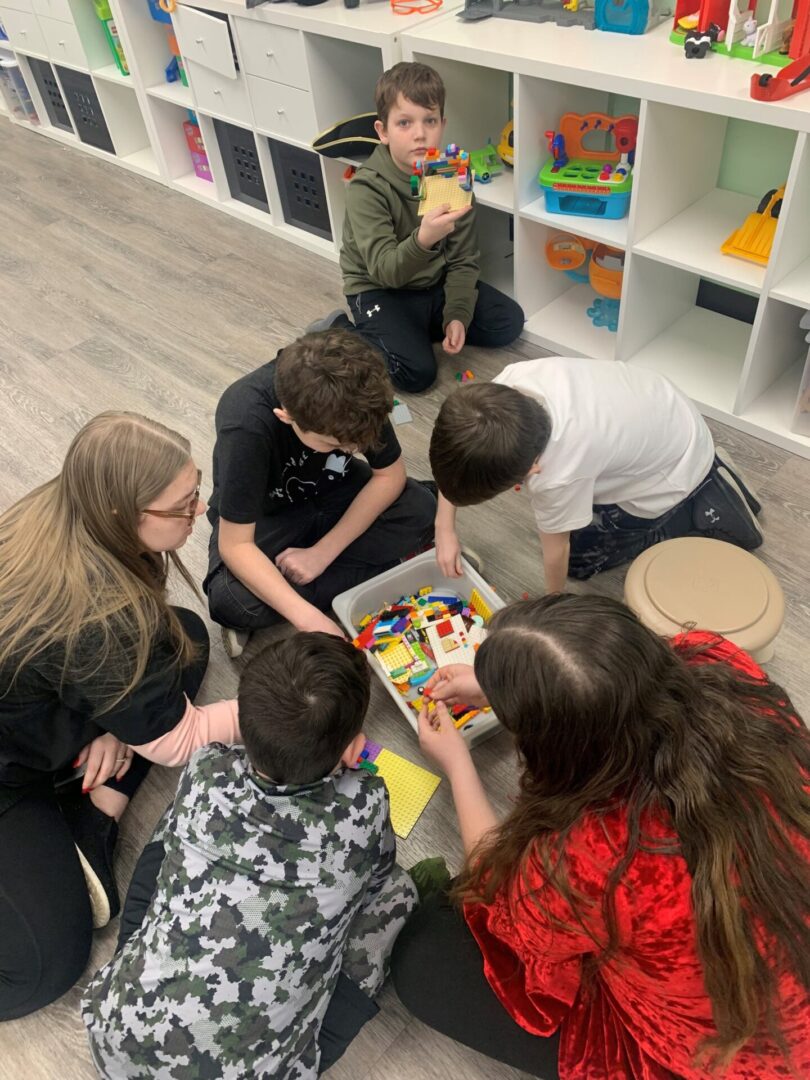
Natural Environmental Training (NET)
NET focuses on practicing and teaching skills within situations that they would rather naturally happen. In these situations, the therapist uses naturally occurring opportunities to help children learn.
The therapist might provide a coloring page but withhold the crayons until the child requests them, give the child an empty cup and wait for them to request juice, or play a board game but withholding the dice or spinner until the child requests it are all examples of using NET. This is our preferred method of therapy as we incorporate generalization from the beginning of the programs into therapy.

Self-Management Training
Self-management training is used to help individuals increase their independence and generalization of skills without always requiring help from a teacher or parent. This technique results in an individual being able to monitor their own behavior. The individual is taught to self-evaluate their behaviors, keep track and monitor behaviors, and provide their own type of reinforcement.
Video Modeling
Video modeling uses repeated presentations of target behaviors so that there is not a lot of change between modeling the target behavior. Video modeling can assist individuals with working on social skills, learning self-help/hygiene tasks, understanding
emotions, etc.

